Interest Rate Risk - Interest Rate Risk Introduction Rho Finance
They are less direct than using bonds because they involve precious metals. There are typically five types of interest rate risk on bonds and debt instruments as follows.

What Is Interest Rate Risk Definition And Meaning Capital Com
The interest rate risks can also be managed with hedging methods.
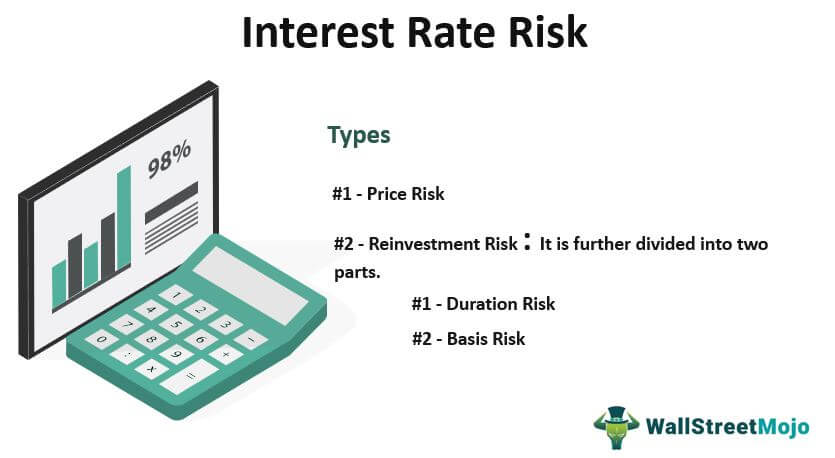
Interest rate risk. The change in a bonds price given the change in interest rates is called its duration. Interest rate risk is the possibility of a loss that could result from a change in interest rates. Repricing Risk Yield Curve Risk Option Risk o Prepayment Extension Risk Basis Risk How financial institutions identify measure monitor and control these risks is critical to an effective IRR Management program.
Longer-term bonds are more sensitive to interest rate changes. Interest Rate Risk Hedging. Interest rate risk is mostly associated with fixed-income assets eg bonds Bonds Bonds are fixed-income securities that.
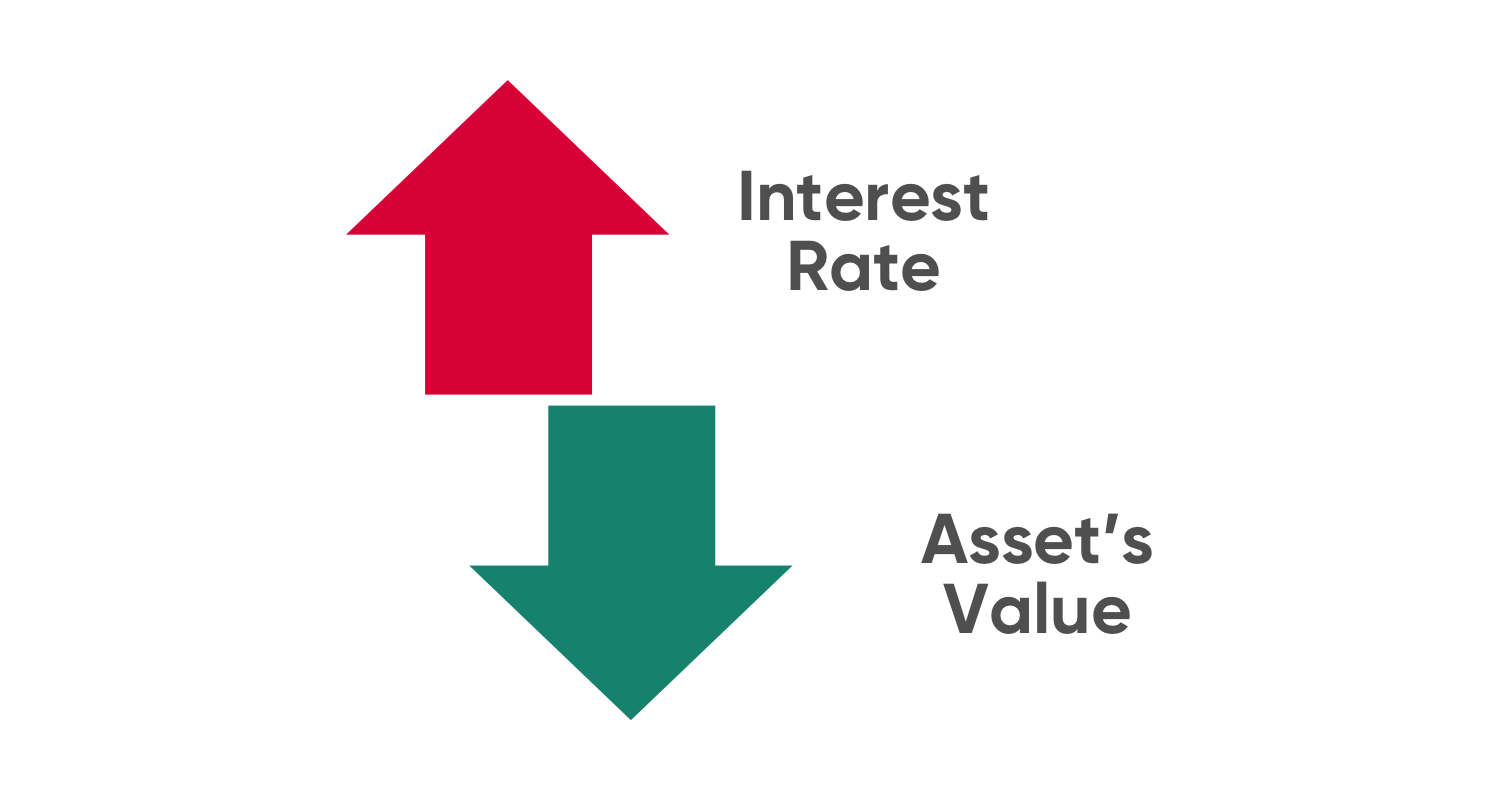
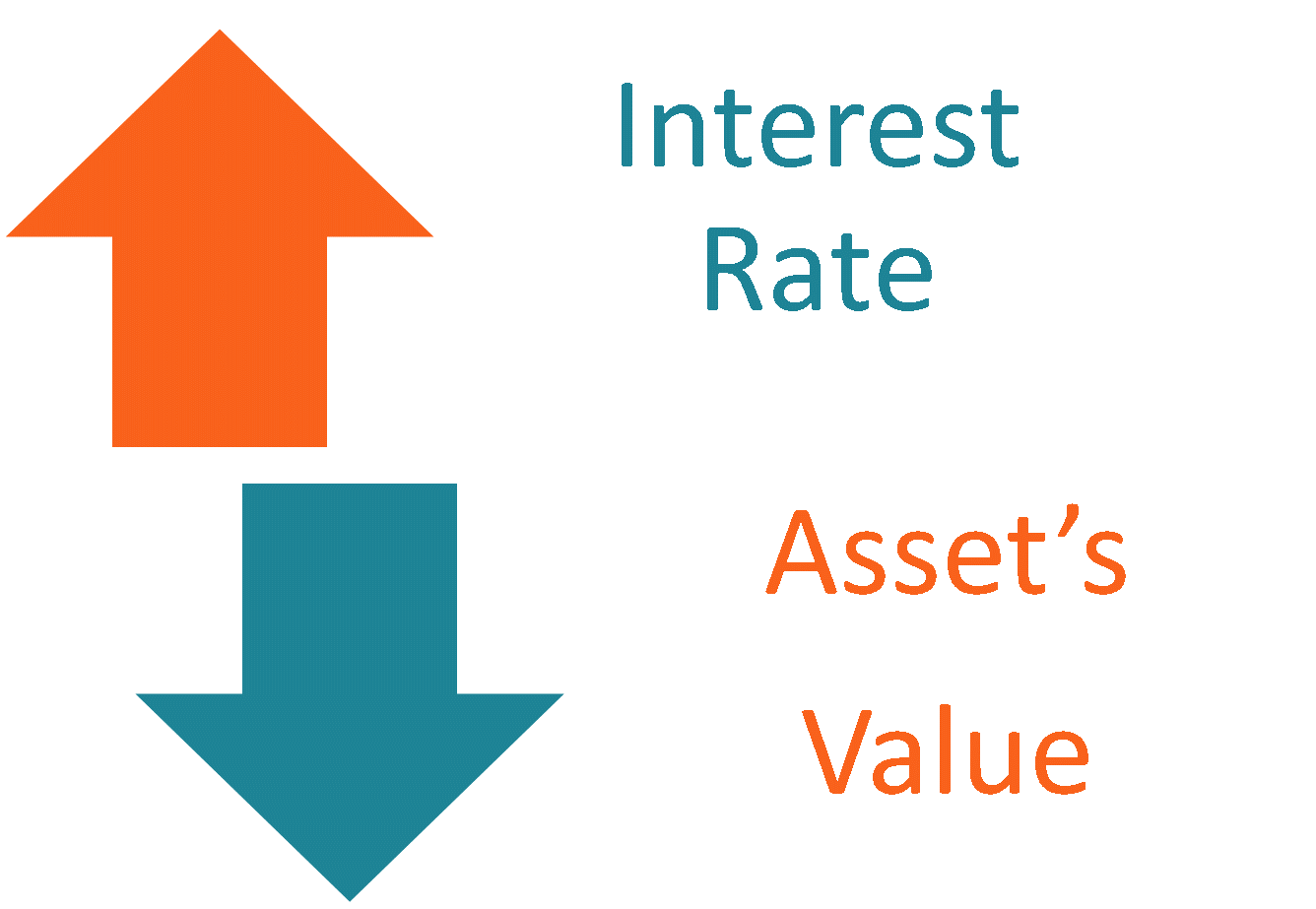
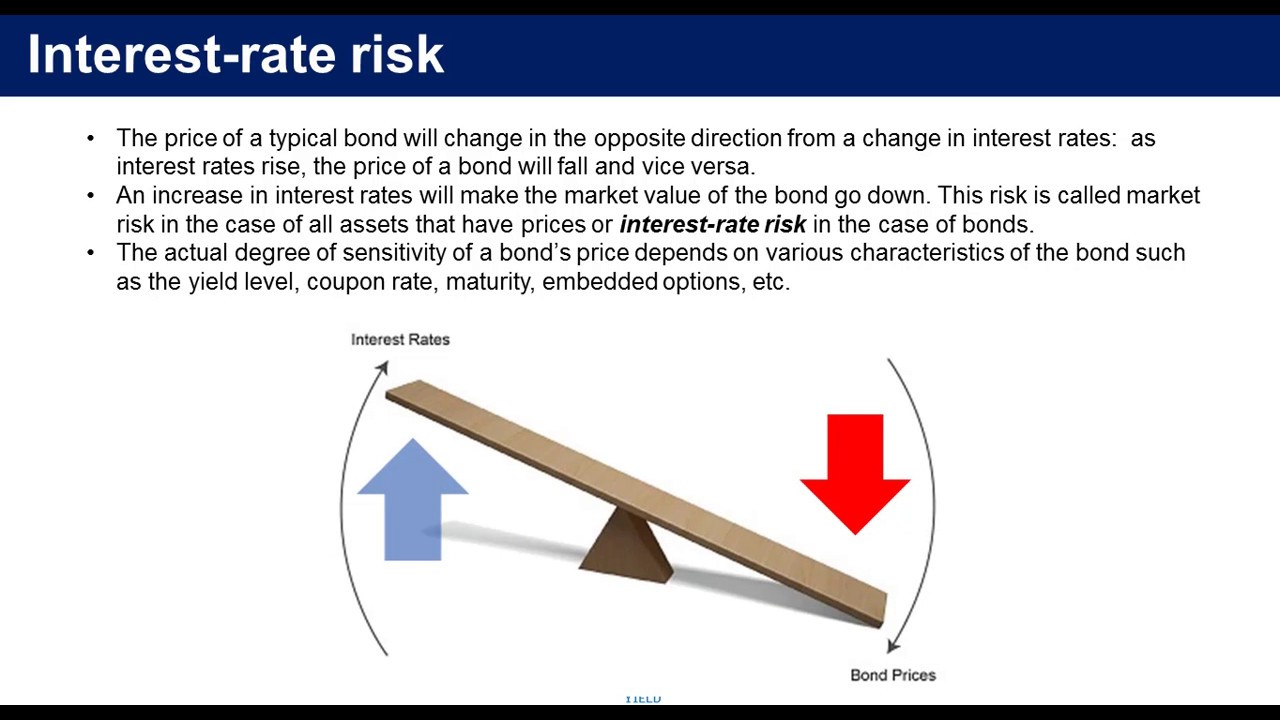
Interest rate risk is the probability of a decline in the value of an asset resulting from unexpected fluctuations in interest rates. Interest rate risk within prudent levels is essential to the safety and soundness of banks. Interest rate risk is the risk or volatility associated with bonds or long term debt as their interest rates coupon yield to maturity and maturity dates move within the market.
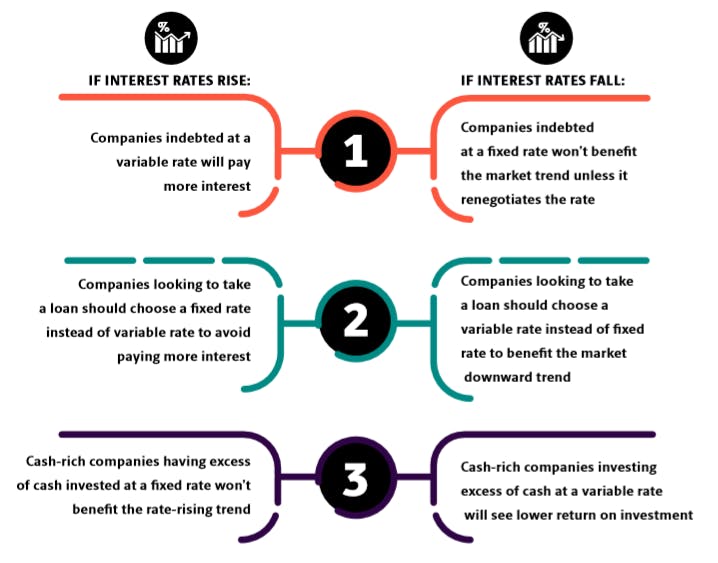
Financial risk can be eliminated or mitigated to an extent with different techniques. The fixed versus floating debate. This risk is most commonly associated with an investment in a fixed-rate bond.
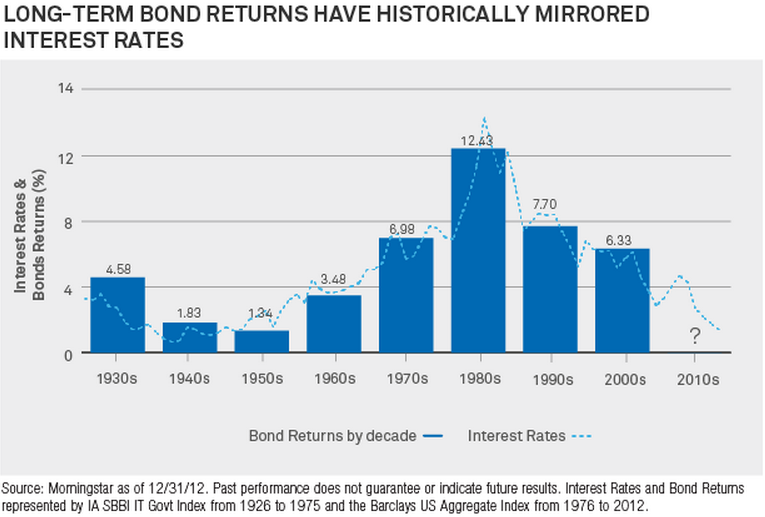
Figure one is a plot many treasurers will be familiar with. Long-term fixed-income securities such as bonds and preferred stock subject their owners to the greatest amount of interest rate risk. When interest rates rise the market value of the bond declines since the rate being paid on the bond is now lower in relation.
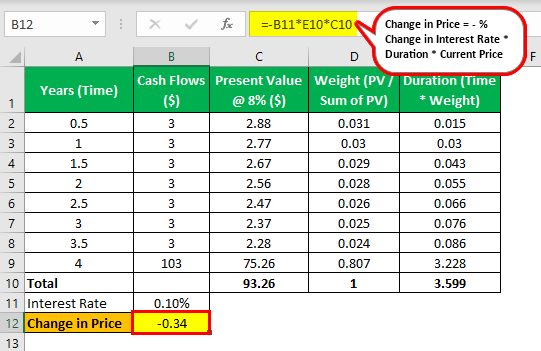
Bonds with longer maturity have a higher risk than a bond of shorter maturity. Interest rate risk. 3 rows Like an interest rate risk example consider that Mr Daljeet invests Rs.
Interest rate risk is the possibility that the value of an investment will decline as the result of an unexpected change in interest rates. Interest rate risk accounts for approximately 90 of the risk involved with fixed income investing according to research by BARRA International. As part of the risk management process the committee will monitor the current risk exposure and duration gap using rate sensitivity analysis and simulation modelling to assess whether the current level of risk is.
Before setting out some principles for interest rate risk management a brief introduction to the sources and effects of interest rate risk might be helpful. Interest Rate Risk has several components including. It generally arises from Repricing risk risks related to the timing mismatch in the maturity and repricing of assets and liabilities and off.
Managing interest-rate risk is in effect the adjustment of risk exposure upwards or downwards which will be in response to ALCOs views on the future direction of interest rates. Precious metal values tend to rise as interest rates move higher which means investors can purchase them as a hedge against higher rates before rates begin rising. The risk that interest rates will rise and reduce the market value of an investment.
Before a business adapts to hedging methods it must consider the cost-benefits attached to it. There are some other methods you can use to reduce interest rate risk. 10000 on bonds of value.
The interest rate risk is the risk arising due to the fluctuation of interest rates. Although analysts and investors spend countless hours analyzing interest rate trends and making forecasts there is no way to tell for sure what rates will be tomorrow. Thus the following sections describe the primary forms of interest rate risk to which banks are.
Interest rate risk in the Banking Book IRRBB is the risk to earnings or capital arising from movement of interest rates. It shows that over a series of consecutive three-year periods going back twenty-five years a floating rate borrower pays off approximately 75 percent of the time versus a three-year fixing for the same period. Short-term securities such as Treasury bills are influenced much less by interest rate movements.
It is pretty common in the markets and investors to keep a close eye on these types of risks to calculate the value of their portfolio including bonds and equity shares. Hedging is the most widely used method for mitigating financial risks. In case the rate increases the value of a bond or other fixed-income security will decline.
Interest Rate Risk Interest Rate Changes Have Significant

Treasury Essentials Interest Rate Risk The Association Of Corporate Treasurers
What Is Interest Rate Risk Definition And Meaning Capital Com
Interest Rate Risk Definition How To Mitigate The Risk

Understanding Interest Rate Risk And How You Can Manage It American Century Investments
Definitive Description Of Interest Rate Risk Reinvestment Risk And Call Risk Youtube
Interest Rate Risk Introduction Rho Finance
Interest Rate Risk Definition Types Interest Rate Risk Example In Bonds
Interest Rate Risk Definition Types Interest Rate Risk Example In Bonds

Interest Rate Risk Management At Community Banks Community Banking Connections

Managing Interest Rate Risk Ppt Powerpoint Presentation Infographics Slide Download Cpb Powerpoint Slides Diagrams Themes For Ppt Presentations Graphic Ideas
Statrys How To Factor Interest Rate Risk In Your Hedging Policy
Interest Rate Risk In The Euro Area

Management Of Interest Rate Risk

Interest Rate Risk Market Interest Rate And Bond Prices Risk Management Guru

Dheeraj Ar Twitter Interest Rate Risk Definition Types Interest Rate Risk Example In Bonds Https T Co Baj3cxektz Interestraterisk Https T Co G1z5kikr5k Twitter